How search behavior is changing?
AI-driven search tools like ChatGPT and Google’s AI Overviews now deliver direct answers, bypassing the need for users to click through to websites. Large language models (LLMs) now sit between content and consumer, delivering a personalized search experience informed by past interactions and removing the cognitive load of sifting through multiple sources.
AI-first search is reshaping how people interact with information. In traditional search, informational intent accounted for more than half of all queries. Now, 37.5% of ChatGPT interactions are generative, with users asking the AI to create, draft, or produce complete outputs. Informational intent has dropped to just 32%, a 20-point decline that challenges decades of SEO practice. Users are bypassing discovery and navigation, going straight to finished results with LLMs acting as both researcher and creator in a single step.
The nature of queries themselves is changing. Users are submitting longer, more conversational prompts, and the responses they receive are increasingly personalized. The same ChatGPT query can produce different answers for different users based on their interaction history, and Google’s AI Overviews show similar behavior. In this environment, the idea of a single, fixed ranking in traditional SERPs starts to lose relevance—every search experience is now dynamic, context-aware, and unique to the individual.
What is LLM SEO / LLMO / GEO?
LLM SEO is the art of becoming the go-to source that AI-powered answer engines like ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, or Perplexity rely on when crafting responses. These platforms don’t just use a single model—they orchestrate several large language models, each fine-tuned for specific tasks, to provide accurate answers that closely match user intent. Instead of competing to rank on page one, your goal is to be part of the content these models read, understand, and pull from to satisfy users’ questions.
How does AI-powered search/answer engines work?
1. User persona
When it comes to LLM SEO, understanding the user persona is key to creating content that truly connects with what a specific user is looking for. User personas go beyond basic demographics—they capture the unique behaviors, preferences, and contexts of individual users.
Google’s own guidelines explain that their search systems use signals like search history, location, and user preferences to personalize and refine results. Similarly, ChatGPT uses its memory feature to not only understand the immediate question but also to tailor responses based on a user’s past interactions and needs. This means AI-powered engines deliver answers that feel more relevant and personalized, making it essential for content creators to think about who their audience really is and what drives their intent.
2. Query fan out
AI-powered answer engines like Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and ChatGPT take user history and persona into account when processing queries. Instead of treating a query as a single unit, they break it down into multiple sub-queries to better understand and address each part. Google explicitly highlighted this approach in their Search IO 2025 presentation.
I tested this with Perplexity, and it clearly performs query decomposition to improve answer quality. This technique of “query fan-out” is essential for delivering precise, relevant responses, and while each engine uses its own methods, the underlying principle is the same across the board.
3. Dense retrieval
Given the sub-queries, they are matched against potentially relevant pages. The exact method isn’t fully transparent, but it likely involves vector similarity between the query and elements like the page title, metadata, and other ranking signals. Once candidate pages are identified, passage-level embeddings are compared to the query embedding to check how closely they align. If the similarity is high, that passage can be selected as a source. Google’s “Method for Text Ranking with Pairwise Ranking Prompting” patent describes a process where an LLM then compares passages in pairs, repeatedly judging which is more relevant to the query, and using those results to refine the final selection.
4. Personalized response
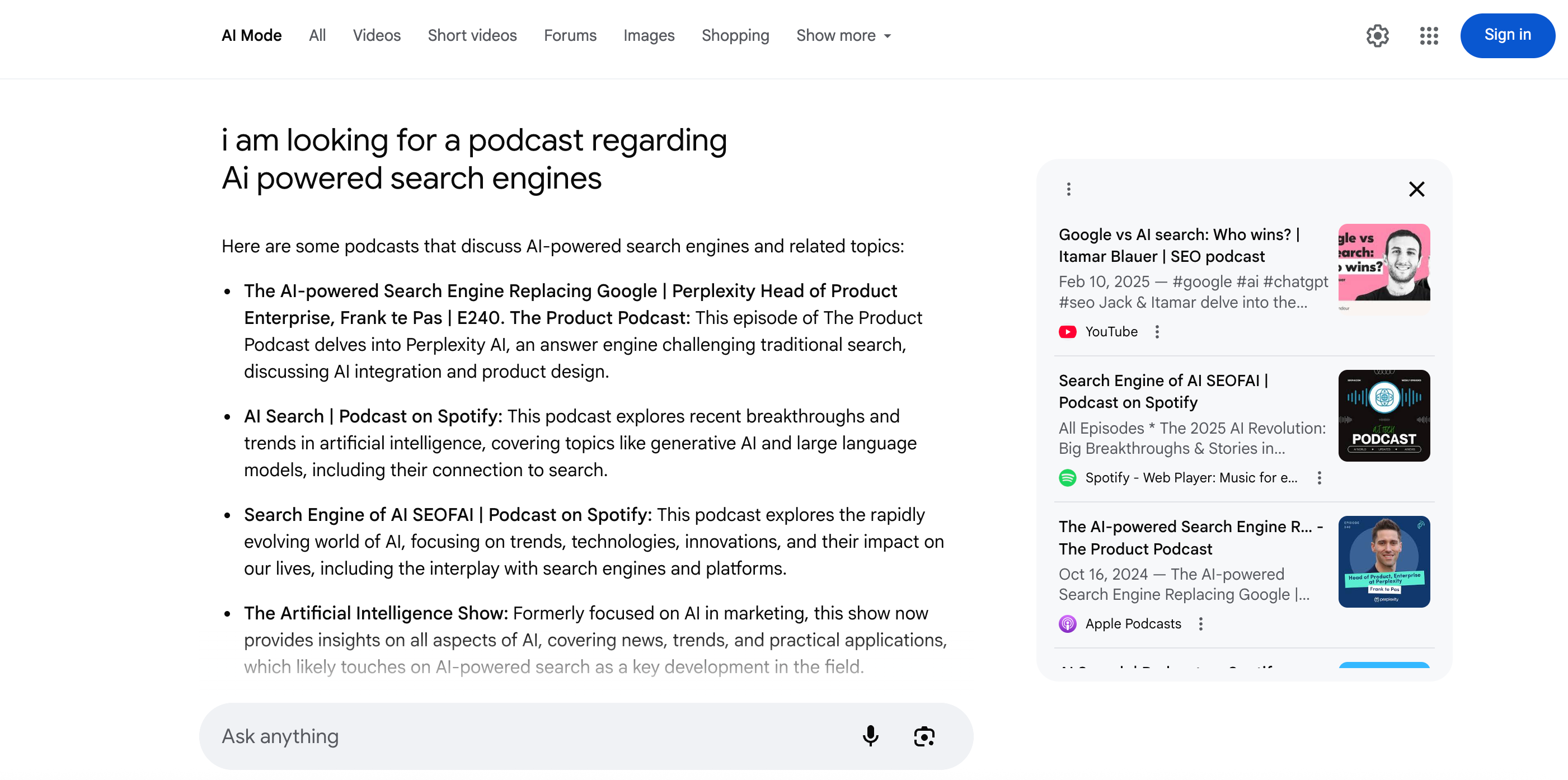
In the final stage, the synthesis model generates an answer by combining its training knowledge with the passages and data it has gathered. It decides dynamically which elements to include—text, lists, carousels, charts—based on the user’s intent and the structure of the available content. For example, when I searched for “I am looking for a podcast regarding AI-powered search engines,” the response included direct links to relevant shows on YouTube, Spotify, and Apple Podcasts, tailoring the output format and sources to meet that specific request.
LLM SEO in Practice: Implementation & Strategy
1. Start with Real User Personas
Build multiple user profiles based on real behaviors—favorite topics, search patterns, preferences. Observe how AI engines like Google AI Overviews display your content for different Personas. Use that insight to refine and align your content with their actual needs.
2. Generate & Target Fan-Out Queries
Use tools like Gemini to generate sub-queries from a single user prompt. Then craft your content to answer each sub-query with clarity and precision, effectively tracing the AI's reasoning path and improving visibility at every step.
3. Ensure Technical Crawlability
To be picked up by AI-powered search systems, your site must be accessible, structured, and interpretable by bots.
Points:
- Use semantic HTML and a clean heading hierarchy (H1 → H3)
- Implement Schema.org markup (FAQPage, TechArticle, etc.) for clarity
- Many AI crawlers don’t execute JavaScript, so you need to ensure your content is crawlable and indexable
4. Be Present Across Platforms
Increase your chances of being cited by appearing on high-signal platforms like Reddit, GitHub, Stack Overflow, and others. From the study from Profound, it shows ChatGPT mostly sources its information from Wikipedia, Google AI Overviews and Perplexity mostly source their information from Reddit.